How NFPA 10 Regulates Portable Fire Extinguishers: A Complete Overview
Portable fire extinguishers are a critical component of fire safety in buildings, workplaces, and vehicles. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) plays a vital role in setting guidelines and standards for fire safety, with it being the primary regulation governing the installation, maintenance, and usage of portable fire extinguishers. In this article, we will explore how NFPA 10 regulates portable fire extinguishers, highlighting key provisions, maintenance requirements, and the importance of compliance in various settings.
What is NFPA 10?
NFPA 10 is the standard for the installation, inspection, maintenance, and use of portable fire extinguishers. Established by the National Fire Protection Association, This standard sets out comprehensive guidelines designed to ensure that fire extinguishers are strategically located, properly maintained, and readily accessible when needed. The regulation applies to a wide range of environments, including residential, commercial, industrial, and vehicular settings.
This outlines the types of extinguishers required for different fire risks, the correct size of extinguishers, and how often they should be inspected or serviced. By following these standards, businesses and homeowners can help prevent and mitigate the effects of fires, reducing the risk of injury and property damage.
Key Objectives of NFPA 10
The primary objectives of NFPA 10 include:
- Ensuring fire extinguishers are available, accessible, and fully operational when needed.
- Establishing a framework for selecting the right type of extinguisher based on the specific hazards in a location.
- Standardizing the maintenance and inspection of extinguishers to ensure reliability and compliance with safety regulations.
By following these objectives, organizations can create safer environments for their employees, customers, and property.
Types of Portable Fire Extinguishers Covered by NFPA 10
One of the core aspects of this NFPA Code is defining the various types of fire extinguishers and when each should be used. Fire extinguishers are classified according to the type of fire they are designed to combat. The most common classifications are:
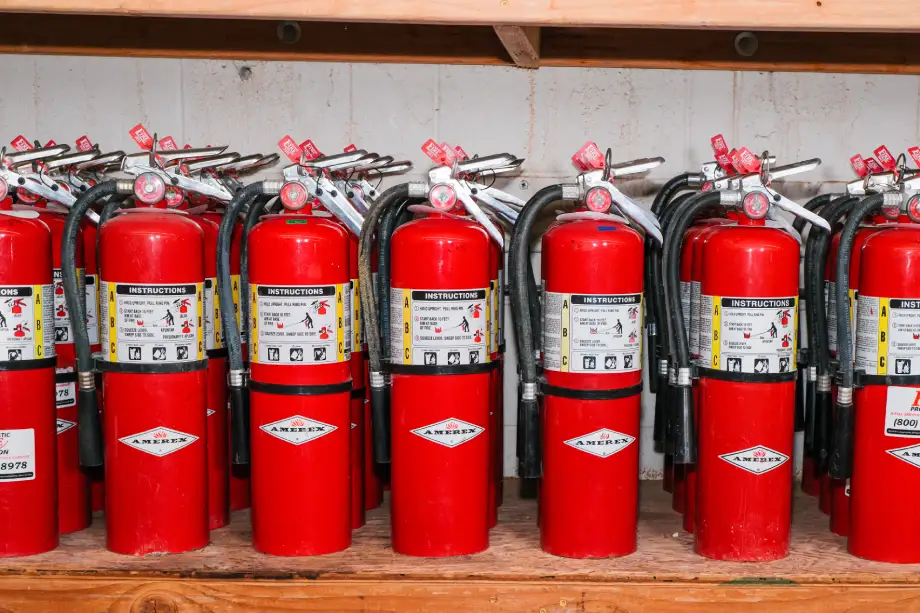


Class B: For flammable liquids and gases, such as gasoline or oil.
Class C: For electrical fires, including those involving live electrical equipment.
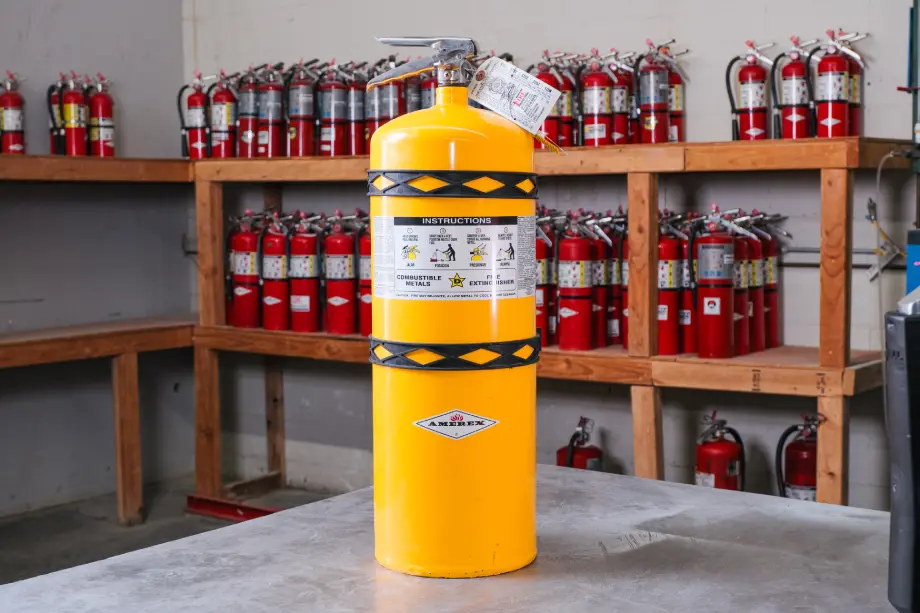
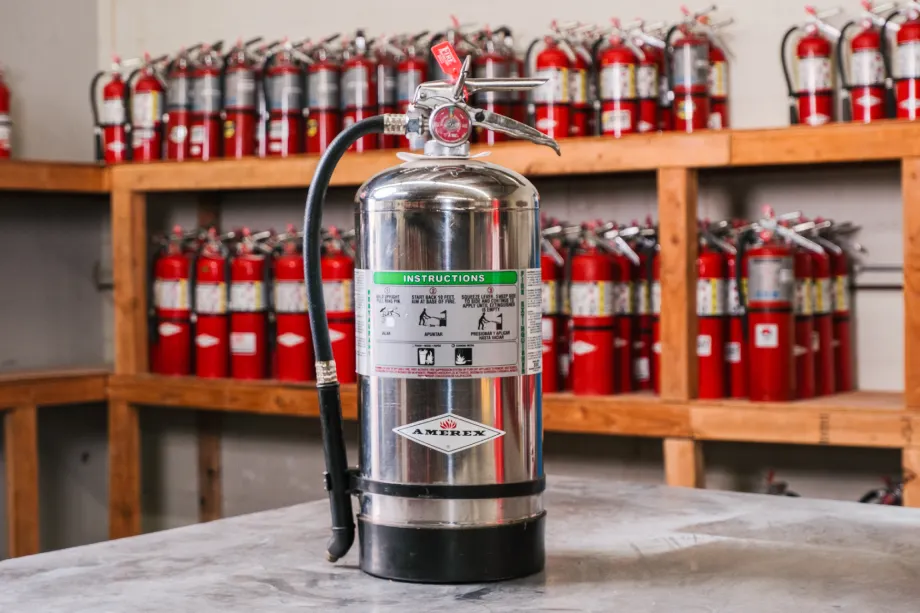




NFPA 10 specifies that the type and size of fire extinguisher required for any given space depend on the nature of the fire hazards present. For instance, kitchens must be equipped with Class K extinguishers, while office spaces typically require Class A or B extinguishers depending on the materials stored.
Choosing the Right Fire Extinguisher
Selecting the correct fire extinguisher is critical to fire safety. NFPA 10 requires that the extinguishers chosen match the potential fire risks in the environment. The key considerations include:
- Size of the area: Larger spaces may require multiple extinguishers.
- Hazard classification: Areas with different types of fire risks will need different classes of extinguishers.
- Accessibility: Fire extinguishers must be easy to locate and within reach of employees or occupants in an emergency.
Proper selection helps ensure that the fire extinguisher will effectively control a fire before it escalates, improving overall safety.
Installation and Location Requirements
The correct placement and installation of portable fire extinguishers are essential components of NFPA 10 regulations. Ensuring that fire extinguishers are easily accessible and visible is critical to their effectiveness in an emergency.
Proper Placement Guidelines
According to NFPA 10, fire extinguishers should be located where they are easily accessible without obstructions. Specific placement requirements include:
- Maximum travel distance: Fire extinguishers should be placed so that the maximum travel distance to an extinguisher does not exceed 75 feet in commercial or industrial settings. This distance may vary in residential areas or in spaces with unique hazards.
- Height: The handle of a fire extinguisher should be located between 3.5 and 5 feet above the floor for easy access by most adults. Larger extinguishers may be mounted lower for easier handling.
- Visibility: Extinguishers should be clearly visible or properly marked with signage to ensure they can be located quickly in an emergency.
By adhering to these placement standards, NFPA 10 ensures that fire extinguishers can be quickly accessed when a fire breaks out, which can be critical in preventing further damage or injury.
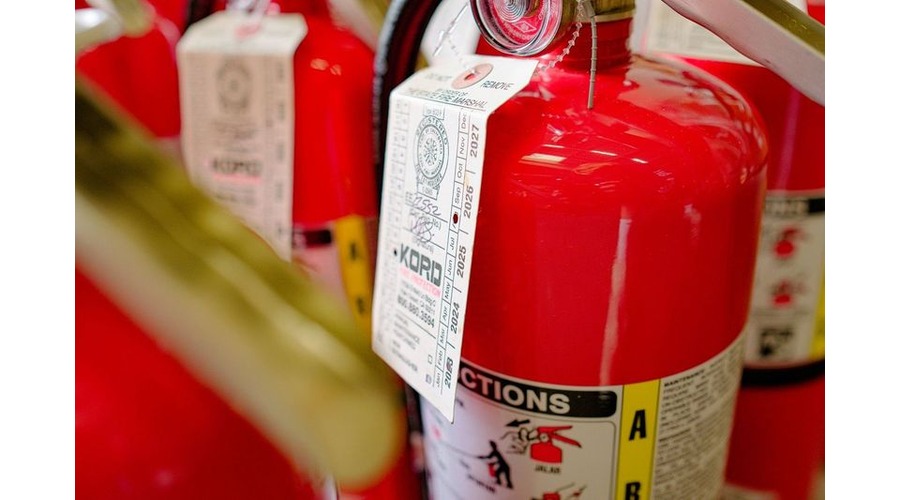
Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
Regular maintenance and inspection of portable fire extinguishers are crucial for ensuring their functionality in case of an emergency. NFPA 10 sets stringent guidelines for the maintenance and inspection process, specifying the frequency and type of checks required.
Inspection and Maintenance Checklist
The NFPA 10 standard outlines both monthly and annual inspection requirements:
- Monthly Inspections: Fire extinguishers should be visually inspected each month to ensure that:
- The pressure gauge is within the recommended range.
- The pin is intact and the tamper seal is unbroken.
- There are no visible signs of physical damage or corrosion.
- The fire extinguisher is in its designated location and accessible.
- Annual Maintenance: Fire extinguishers must undergo a more thorough inspection once per year by a qualified professional. This includes:
- Checking the extinguisher’s internal components.
- Ensuring that it is fully charged and that it will discharge properly in case of an emergency.
- Refilling or replacing the extinguisher if necessary.
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure that the extinguisher is not only functional but also effective at putting out a fire.
Compliance with NFPA 10: Legal and Insurance Implications
Failure to comply with NFPA 10 can have serious legal and financial consequences. In many jurisdictions, compliance with NFPA 10 is a legal requirement for businesses, particularly those with higher fire risks. Non-compliance can lead to:
- Fines and penalties: Businesses may face fines for failing to adhere to fire safety regulations.
- Increased liability: In the event of a fire, failure to maintain or properly install fire extinguishers can lead to increased liability in the case of injury or property damage.
- Insurance complications: Insurance companies may refuse to cover damages if it is found that the business did not comply with fire safety standards, including those outlined in NFPA 10.
By following NFPA 10 regulations, businesses and property owners can protect themselves from legal, financial, and reputational risks associated with non-compliance.
Key Takeaways
- NFPA 10 sets the standards for portable fire extinguishers, covering installation, maintenance, and use.
- Fire extinguishers must be selected based on the specific fire hazards present in each environment.
- Regular inspections and maintenance are required to ensure that fire extinguishers remain functional and ready for use.
- Non-compliance with NFPA 10 can result in legal consequences, insurance issues, and heightened fire risks.
NFPA Portable Fire Extinguishers FAQs
Contact an expert today. Its free!
Ensuring that NFPA 10 regulates portable fire extinguishers effectively is essential for maintaining fire safety across all environments. By understanding and adhering to NFPA’s standards for fire extinguisher installation, maintenance, and inspection, businesses, homeowners, and institutions can mitigate the risk of fire-related injuries and property damage. Regular maintenance, proper placement, and compliance with these standards help ensure that fire extinguishers remain functional and ready when needed most.