An Overview Of The NFPA 11 Standard For Foam Fire Extinguishing Systems
The NFPA 11 Standard, published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), sets forth guidelines for foam fire extinguishing systems, which are vital for protecting lives, property, and the environment from flammable liquid fires. Understanding this standard is essential for anyone involved in fire safety, engineering, or risk management. In this article, we will explore the NFPA 11 Standard’s key provisions, its purpose, its application, and how it interacts with other NFPA standards, offering an in-depth look into its role in fire safety.
Introduction to the NFPA 11 Standard
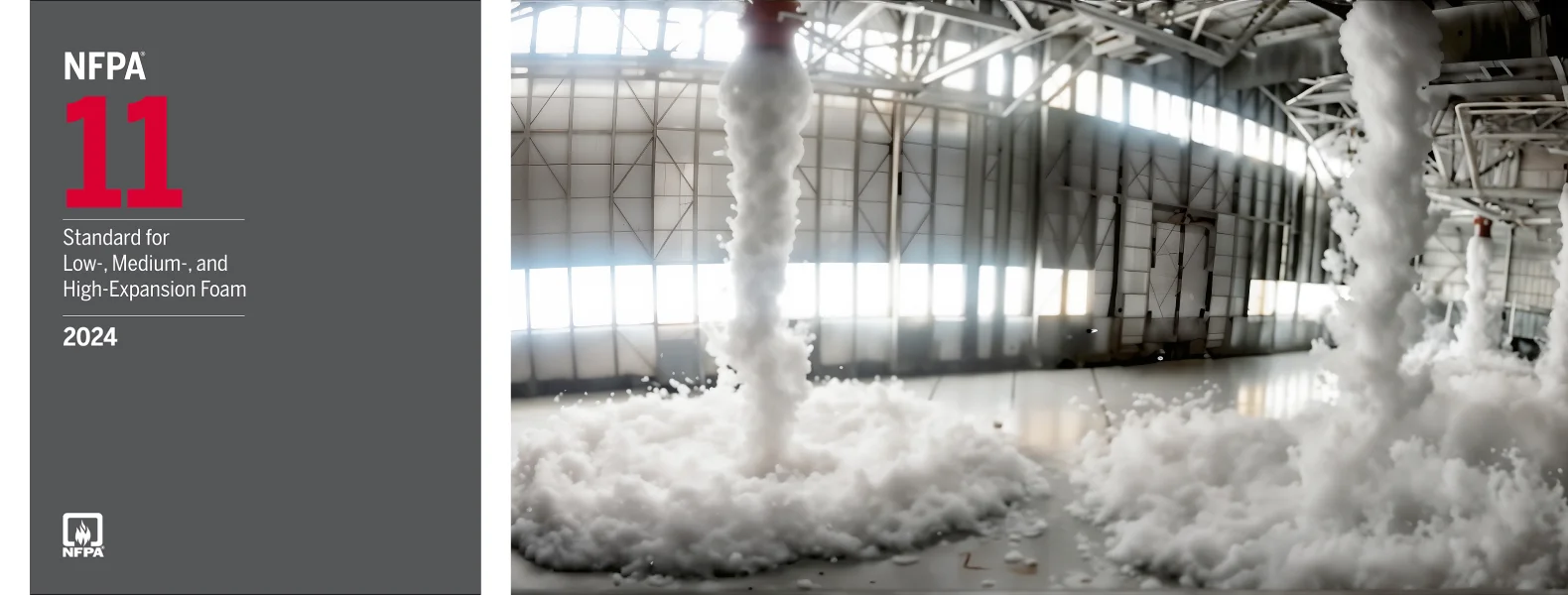
The NFPA 11 Standard provides comprehensive guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of foam fire extinguishing systems, which are primarily used to suppress fires involving flammable liquids and gases. The NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) is a recognized leader in fire safety standards, and NFPA 11 is one of its key standards that directly addresses fire protection systems utilizing foam.
The NFPA 11 Standard ensures that foam systems are properly designed to handle a range of fire scenarios, providing vital protection in industries such as oil and gas, aviation, manufacturing, and chemical processing. By establishing guidelines for various foam types, application methods, and system configurations, the standard ensures that foam fire extinguishing systems are both effective and reliable in critical fire situations.
Key Components of the NFPA 11 Standard
The NFPA 11 Standard outlines specific guidelines for foam systems, which are divided into several core components. These components include foam concentrates, foam discharge devices, system design, and the proper installation and maintenance protocols for foam systems. Below is an overview of the most crucial elements:
1. Types of Foam Concentrates
The NFPA 11 Standard distinguishes between different types of foam concentrates, including:
- Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF): Ideal for flammable liquid fires such as gasoline and other hydrocarbon fuels.
- Alcohol-Resistant Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AR-AFFF): Designed for fires involving polar solvents like alcohols and acetones.
- High Expansion Foam: Used in confined spaces, this foam expands significantly and is useful for covering large areas.
Each type of foam concentrate is suited for particular fire scenarios, and the standard specifies the appropriate foam concentrate to be used for each application.
2. System Design and Configuration
The NFPA 11 Standard provides guidelines for the design of foam extinguishing systems, including the selection of foam type, the placement of foam discharge devices, and system configuration. The design ensures the foam system will provide adequate coverage over the designated risk area. These systems can be either fixed or portable, with fixed systems being the most common in industrial settings.
The foam discharge devices must be strategically placed to ensure effective foam coverage, and the foam system must be sized appropriately based on the risk involved and the area that needs protection. The standard also mandates regular testing to ensure that foam systems maintain peak performance during an emergency.
3. Testing and Maintenance
The NFPA 11 Standard emphasizes the importance of regular testing and maintenance to ensure foam systems remain functional. Foam concentrates must be tested for effectiveness, and all system components, such as foam proportioners, tanks, and pumps, must be inspected and maintained according to established protocols. Routine maintenance helps prevent malfunctions during fire emergencies, ensuring that foam systems perform as expected.
4. Application Methods
The standard outlines various application methods, such as deluge systems, wet systems, and dry systems, each tailored to different types of facilities and fire risks. Deluge systems are commonly used in high-risk areas where rapid fire suppression is required. The application method should be chosen based on the specific hazards and requirements of the facility.
NFPA 11 Standard in 2024: What Has Changed?
The NFPA 11 Standard in 2024 has undergone updates to keep pace with evolving fire safety technology and emerging threats. New revisions typically address the latest advances in foam technologies, new fire risks, and the ongoing evolution of fire safety best practices. Key updates to the 2024 version include:
- Improved Environmental Considerations: Increased attention is being paid to the environmental impact of foam agents, particularly with the growing concerns over fluorinated compounds found in some foam concentrates. The NFPA has worked to standardize the use of fluorine-free foam in certain settings, addressing concerns regarding groundwater contamination and human health risks.
- Enhanced Performance Standards: Stricter requirements have been implemented to improve the performance of foam systems, particularly with regard to their ability to quickly suppress large-scale flammable liquid fires. These performance standards also focus on minimizing the time required for a foam system to activate and achieve complete suppression.
- Increased Flexibility in System Design: The 2024 revisions have provided greater flexibility in system design to accommodate a broader range of industrial and commercial environments. The revised standard allows for more customization in foam application methods, based on the unique risks of different facilities.
These updates reflect the ongoing commitment of the NFPA to maintain the relevance and effectiveness of its standards as fire safety technologies and practices evolve.
The Role of Foam Systems in Fire Safety
Foam fire extinguishing systems are critical in certain industrial sectors where traditional fire suppression methods like water are insufficient or inappropriate. The NFPA 11 Standard is instrumental in ensuring that foam systems meet rigorous safety standards. Key industries that rely on foam systems include:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector faces heightened risks of fires due to the presence of flammable liquids and gases. In these settings, foam fire extinguishing systems are designed to quickly suppress fires and limit property damage. Foam systems, governed by the NFPA 11 Standard, help mitigate the severe consequences of hydrocarbon fires.
2. Aviation
Airports and aviation facilities use foam systems for aircraft fire protection. Since aviation fuel is highly flammable, foam systems help reduce the risk of catastrophic fires during emergencies. The NFPA 11 Standard is used to design foam systems that are tailored to the specific needs of airport and aviation operations.
3. Chemical Manufacturing
Chemical manufacturing facilities, where hazardous substances are processed or stored, also depend on foam fire suppression systems. The NFPA 11 Standard ensures that these systems are designed to handle a variety of flammable chemicals and substances that pose unique fire hazards.
Other Related NFPA Standards
While NFPA 11 is focused on foam systems, it works in conjunction with other NFPA standards to provide a comprehensive fire protection approach. Key standards include:
- NFPA 13 – Installation of Sprinkler Systems: Often used alongside foam systems in industrial settings to provide an additional layer of fire suppression.
- NFPA 25 – Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance of Water-Based Fire Protection Systems: Ensures the reliability of other fire protection systems.
- NFPA 30 – Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code: Provides guidance on the safe storage, handling, and use of flammable liquids that foam systems often protect against.
Together, these standards work to ensure a holistic approach to fire safety, integrating foam systems with other fire protection technologies.
NFPA 11 FAQS
Key Takeaways
The NFPA 11 Standard provides essential guidelines for foam fire extinguishing systems used in industries dealing with flammable liquids and gases.
It covers system design, foam concentrates, discharge devices, maintenance, and testing protocols.
Updates in 2024 reflect advancements in technology, environmental concerns, and the evolving nature of fire risks.
Get Top-Rated Fire Safety Solutions!
Kord Fire Protection is your go-to when it comes to all things fire protection. For over 20 years, we’ve been serving Southern California with the quality service and equipment to keep your home or business safe at all times. Our competitive prices reflect our unwavering commitment to protecting what matters most in the event of a fire emergency. Give us a call, send an email, or use that form!


Protect Your Property
Get the latest fire safety tips delivered straight to your inbox.